Social Determinants of Health: Factors, Impact, and FAQs
Health is not only shaped by genetics and medical care but also by a broader set of social, economic, and environmental factors. These factors, known as social determinants of health (SDOH), significantly influence a person’s overall well-being, access to healthcare, and quality of life.
This article delves into what social determinants of health are, their impact, real-world examples, and solutions to reduce health disparities caused by these determinants.
What Are Social Determinants of Health?
Social determinants of health are the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These determinants are shaped by the distribution of resources, power, and opportunities in a society.
Examples of Social Determinants of Health:
- Income and social status
- Education access and quality
- Employment and working conditions
- Social support networks
- Physical environment (housing and neighborhood)
- Access to healthcare
- Food security
Definition (WHO):
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), social determinants of health are the circumstances in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, and the systems put in place to deal with illness.
Why Do Social Determinants of Health Matter?
Social determinants significantly affect an individual’s physical and mental health. People with limited access to resources often experience worse health outcomes, shorter life expectancy, and higher rates of chronic diseases.
Key Reasons They Matter:
- Health Disparities: SDOH explain why some groups experience higher rates of illness and mortality than others.
- Preventable Inequalities: Many health inequalities caused by SDOH can be addressed through better policies and interventions.
- Impact on Healthcare Systems: Addressing SDOH reduces healthcare costs by preventing illnesses caused by poor social conditions.
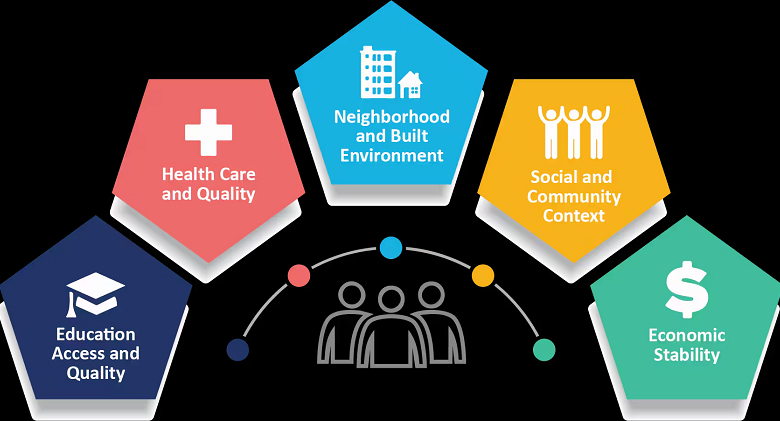
Major Categories of Social Determinants of Health
The social determinants of health are often categorized into five key areas, commonly referred to as the Healthy People 2030 Framework:
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Stability | The ability to afford basic needs like food, housing, and healthcare. | Employment, income, financial stress, poverty. |
| Education Access & Quality | Education impacts health literacy, job opportunities, and decision-making skills. | School quality, literacy, higher education. |
| Healthcare Access & Quality | Availability and affordability of healthcare services. | Insurance, proximity to healthcare providers. |
| Neighborhood & Built Environment | Living conditions that affect safety, housing, and access to resources. | Housing quality, transportation, green spaces. |
| Social & Community Context | Social relationships and community support that influence mental and physical health. | Social networks, discrimination, civic engagement. |
Economic Stability
A person’s income and financial security have a significant impact on health. People in low-income households often lack access to adequate healthcare, nutritious food, and safe housing.
- Example: Chronic diseases such as diabetes are more prevalent in low-income communities where access to healthy food options is limited.
Solutions:
- Increasing minimum wages.
- Expanding employment opportunities.
- Providing financial assistance for basic needs like housing.
Education Access and Quality
Education improves health by increasing knowledge, skills, and economic opportunities. Poor access to education can lead to lower health literacy, limited career options, and higher rates of chronic illness.
- Example: Individuals with higher education levels are less likely to smoke and more likely to engage in healthy behaviors.
Solutions:
- Investing in early childhood education programs.
- Improving school funding in underserved areas.
- Promoting health education in schools.
Healthcare Access and Quality
Quality healthcare ensures that individuals receive preventive services, proper diagnosis, and effective treatments. However, barriers such as cost, location, and lack of health insurance can restrict access.
- Example: Rural populations often face challenges accessing healthcare facilities, resulting in delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Solutions:
- Expanding healthcare coverage and subsidies.
- Increasing the number of healthcare providers in underserved areas.
- Enhancing telehealth services to reach remote communities.
Neighborhood and Built Environment
Where people live affects their safety, access to resources, and overall quality of life. Poor living conditions can lead to stress, injury, and exposure to pollutants.
- Example: Individuals living in areas with poor air quality are at higher risk of respiratory diseases.
Solutions:
- Investing in affordable housing.
- Improving public transportation systems.
- Creating green spaces and safe walking paths.
Social and Community Context
Strong social connections improve mental health, reduce stress, and encourage healthy behaviors. Conversely, isolation, discrimination, and lack of community support can harm health.
- Example: Studies show that social isolation increases the risk of heart disease and depression.
Solutions:
- Promoting community engagement programs.
- Reducing discrimination through policy reform.
- Providing mental health support services.
The Impact of Social Determinants on Health
Social determinants contribute to significant health disparities among different population groups. Here’s how these factors can influence various aspects of health:
| Health Outcome | Influencing Determinants |
|---|---|
| Chronic Diseases | Limited access to healthy food and healthcare increases the prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. |
| Mental Health | Social isolation, discrimination, and financial stress can lead to anxiety and depression. |
| Infant Mortality | Poor maternal education and inadequate prenatal care contribute to higher infant mortality rates. |
| Life Expectancy | Income inequality and unsafe living environments can reduce overall life expectancy. |
Real-World Examples of Addressing Social Determinants
Several initiatives and policies have successfully addressed social determinants to improve public health:
- Medicaid Expansion in the U.S.:
- Expanded healthcare coverage to low-income individuals, improving access to preventive care.
- Healthy Food Financing Initiative (HFFI):
- Provides funding to increase access to healthy food in underserved communities, reducing rates of obesity and related diseases.
- Housing First Programs:
- Focus on providing stable housing to homeless individuals, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- School-Based Health Programs:
- Integrate health services into schools to address education and healthcare disparities among children.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health: Solutions and Strategies
Policy Changes
Governments can implement policies to address inequalities, such as:
- Increasing access to affordable housing.
- Expanding Medicaid and universal healthcare programs.
- Raising the minimum wage.
Community-Based Initiatives
Local organizations play a key role in addressing SDOH by offering:
- Food banks and nutrition programs.
- Support groups to foster social connections.
- Transportation assistance for healthcare appointments.
Collaboration Across Sectors
Healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations must work together to create holistic solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the social determinants of health?
A: Social determinants of health are the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes, such as income, education, and living conditions.
Q2: Why are social determinants important for health?
A: They affect access to healthcare, lifestyle choices, and exposure to risks, contributing to overall health disparities.
Q3: Can social determinants be changed?
A: Yes, with targeted policies, community programs, and investments in education, housing, and healthcare, disparities caused by social determinants can be reduced.
Q4: How do social determinants affect mental health?
A: Factors like social isolation, discrimination, and financial stress increase the risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
Q5: What role does education play in health?
A: Education improves health literacy, job opportunities, and decision-making skills, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Conclusion
Social determinants of health play a crucial role in shaping well-being, influencing everything from chronic disease risk to life expectancy. Addressing these factors requires collective action from policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities to create equitable access to resources and opportunities.